Collection: Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC)
Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC)
Whey protein concentrate (WPC) is a dairy-based protein derived from cow's milk. This type of protein supplement is typically made up of around 80% protein, with fats and carbohydrates making up the remaining 20%. Whey concentrate powder is a great way to increase your daily protein intake, as it's easy to consume as a shake or smoothie. It can also be used in baking.
So if you are looking to add more protein to your diet, whey concentrate is a great option. This type of protein is easy to digest and absorb, making it a perfect choice for those looking to build muscle or improve their athletic performance.
Whey concentrate is a healthy source of calories, lower than that of fat, so it's a great option for those who are trying to lose weight. Increasing your protein intake can help you feel fuller for longer, which is a huge benefit for anyone on a calorie-controlled diet.
When it comes to protein supplements, whey protein concentrate is one of the most popular options on the market. At Elite Supplements, we stock one of the widest ranges of whey protein concentrate in Australia from industry-leading brands, so you can find the perfect one for your needs.
Australia's favourite fitness supplement store
Whether you're looking to bulk up, build muscle, or just improve your overall health, Elite Supplements has the right protein concentrate for you.
We offer a huge range of products, a skilled team who can provide you with personalised advice, and a 30-day money-back guarantee on every order.
Our aim is to help you achieve your health and fitness goals to become the best possible version of yourself.
We do this by supplying the best range of whey protein in Australia alongside other supplements, including pre-workout and weight-loss blends, vitamins, protein bars, drinks, and more.
Buy whey protein at the best prices
As Australia's leading supplier of health and fitness supplements, we are able to offer competitive pricing and regular special offers. We're also often the first to stock the latest and most advanced supplements in the country.
Maintaining a healthy diet and building the body of your dreams doesn’t have to cost a fortune. But consuming a lot of high-quality protein sources such as beef, chicken, and fish can result in a hefty grocery bill.
This is where whey protein comes in — it provides a convenient, affordable way to increase your daily protein intake without having to eat more food.
At Elite Supplements, we believe that everyone should have access to the best quality supplements, no matter their budget. So whether you're looking for a high-end WPC protein powder with added ingredients for optimal performance or simply want to buy whey protein concentrate to help you meet your nutritional needs, we have you covered.
Check out our range of whey concentrate protein powders and see for yourself how we can help you achieve your fitness goals on a budget.
FAQ
Whey protein concentrate is a great source of high-quality protein that can help you reach your fitness goals. (1).
Whey has been shown to promote muscle growth and improve strength when used in combination with weight training. Whey may also help to reduce blood pressure and stabilise blood sugar levels. (2, 3, 4).
As protein is more filling than carbohydrates or fats, whey protein concentrate can help you feel fuller for longer, leading to less snacking and reduced calorie intake. This can help you stick to a weight-loss diet and lose excess fat more easily. (5).
Whey protein can be consumed in a number of ways. The most popular method is mixing it with water or milk to create a shake or smoothie. Whey powder can also be added to recipes such as pancakes, muffins, and oatmeal.
Whey protein concentrate is not specifically designed for weight gain. However, it can help you achieve your calorie goals as it's often easier to supplement your diet with shakes than to eat more meat or other high-protein foods. (6).
If you're looking to gain weight, it's important to also focus on increasing your calorie intake through a balanced diet and by undertaking regular weight training.
There isn't necessarily one type of whey protein that's better than the other. Iso whey protein powder is a purer form of whey as it contains less fat and lactose than whey concentrate. However, whey concentrate is often cheaper and still provides a high-quality source of protein. Ultimately, the best type of whey protein for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. (7).
While whey protein is most beneficial when combined with regular exercise, it can still provide some benefits if you don't work out. WPC protein is an easy and convenient way to meet your daily protein needs, which can help to boost your metabolism and support muscle growth. (8, 9).
Whey protein is made from milk and is very safe to consume. It's fine to drink it every day as long as you're eating a balanced diet as well.
The recommended amount of protein you should consume each day depends on your age, gender, and activity level. The Australian government recommends that adult males consume 0.84g per kilogram of body weight and adult females consume 0.75g per kilogram of body weight.
If you're pregnant or breastfeeding, you may need more protein. Athletes and people who exercise regularly also often require more protein than sedentary individuals. (10)
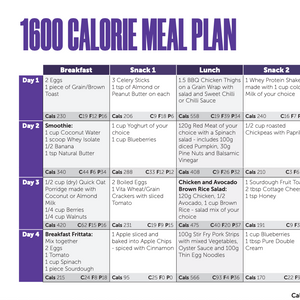
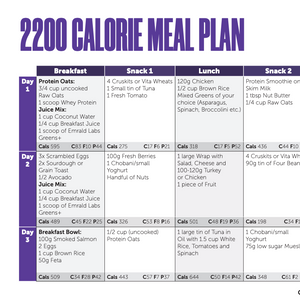
To get the most out of WPC, consume it alongside regular exercise and a balanced diet. If you're looking to build muscle, take whey protein before and after your workouts. And if you're trying to lose weight, drink a shake for breakfast or as a snack between meals. You can also add whey powder to pancakes, muffins, and other recipes to increase your daily protein intake.
You can drink a whey protein concentrate shake at any time of the day to help regulate your appetite and meet your daily protein goal.
However, if you're trying to build muscle or have optimal recovery, it's best to consume whey concentrate protein within one hour of finishing your workout. This can help repair and rebuild your muscles after exercise and ensure you get the maximum benefit from the protein. (11)
Whey is naturally gluten-free. However, some whey protein products may contain traces of gluten if they are manufactured in a facility that also processes gluten-containing foods.
If you're sensitive to gluten or have coeliac disease, it's important to check the label of your whey protein powder to make sure it doesn't contain any traces of gluten.
WPC is made from milk and contains lactose. If you're lactose-intolerant, it's best to choose a whey protein isolate instead of WPC. Whey isolate is a purer form of whey protein that contains less lactose than whey concentrate.
Alternatively, you could opt for a vegan protein powder that uses plant-based ingredients.
In its basic form, concentrate protein powder doesn't taste like much (it's similar to watered-down milk). However, whey protein powders come in a variety of delicious flavours, including chocolate, vanilla, and strawberry. You can also add whey powder to smoothies and other recipes to change up the flavour.
The shelf life of whey protein concentrate varies depending on the manufacturer. However, most WPC powders will last for 9 to 19 months after opening, as long as they are stored in a cool, dry place.
Whey protein should be safe for kids to consume if they need a protein supplement. However, you should always consult your doctor before giving WPC to a child.
Most whey protein concentrates are designed for the nutritional needs of adults. However, some brands have now created protein products specifically for kids, such as the Obvi Kids Complete Protein, which we sell at Elite Supplements.
Protein shakes make a great meal replacement if you're looking to lose weight. They're high in protein and low in calories, making them a good option for people who are trying to slim down. (12)
You can also drink a whey protein shake as a snack between meals if you're feeling hungry. If you're trying to increase your calorie intake or want to boost the nutritional content of your shake, you can add fresh or frozen fruit, yoghurt, nuts, and seeds.
It's important to do your research and find a whey protein powder that matches your dietary needs and flavour preferences.
At Elite Supplements, we offer a wide variety of brands and flavours so you can find the perfect WPC whey protein for you. Some of our best-selling brands include BioTechUSA's 100% Whey, Max's Anabolic Night Slow-Release Protein, ON Whey Concentrate, and Nitrovol Lean Muscle Recovery Protein.
For some people, protein powder may be easier to digest than meat. This is because protein powder is a concentrated source of protein and doesn't contain the tough fibres found in meat that can be difficult to digest. (13, 14).
However, some people do find protein powder can cause digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhoea. If you have trouble digesting protein powder, try a different brand or consider opting for a plant-based protein powder instead.
Elite Supplements stocks several popular brands of whey concentrate powder, including Emerald Labs, BioTechUSA, EHP Labs, and more. As Australia's favourite fitness supplements store, we offer a wide range of protein products to suit your individual needs. You can shop online or in-store at one of our convenient locations across Australia.
References
1. Cintineo, H. P., Arent, M. A., Antonio, J., & Arent, S. M. (2018). Effects of Protein Supplementation on Performance and Recovery in Resistance and Endurance Training. Frontiers in nutrition, 5, 83. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2018.00083
2. McGlory, C., Devries, M. C., & Phillips, S. M. (2017). Skeletal muscle and resistance exercise training; the role of protein synthesis in recovery and remodeling. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 122(3), 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00613.2016
3. Yang, J., Wang, H. P., Tong, X., Li, Z. N., Xu, J. Y., Zhou, L., Zhou, B. Y., & Qin, L. Q. (2019). Effect of whey protein on blood pressure in pre- and mildly hypertensive adults: A randomized controlled study. Food science & nutrition, 7(5), 1857–1864. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1040
4. Frid, A. H., Nilsson, M., Holst, J. J., & Björck, I. M. (2005). Effect of whey on blood glucose and insulin responses to composite breakfast and lunch meals in type 2 diabetic subjects. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 82(1), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn.82.1.69
5. Leidy, H. J., Tang, M., Armstrong, C. L., Martin, C. B., & Campbell, W. W. (2011). The effects of consuming frequent, higher protein meals on appetite and satiety during weight loss in overweight/obese men. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 19(4), 818–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.203
6. Helms, E. R., Aragon, A. A., & Fitschen, P. J. (2014). Evidence-based recommendations for natural bodybuilding contest preparation: nutrition and supplementation. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 11, 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-11-20
7. A Castro, L. H., S de Araújo, F. H., M Olimpio, M. Y., B de B Primo, R., T Pereira, T., F Lopes, L. A., B S de M Trindade, E., Fernandes, R., & A Oesterreich, S. (2019). Comparative Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Concentrated, Hydrolyzed, and Isolated Whey Protein Supplementation on Body Composition of Physical Activity Practitioners. Nutrients, 11(9), 2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092047
8. Graf, S., Egert, S., & Heer, M. (2011). Effects of whey protein supplements on metabolism: evidence from human intervention studies. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 14(6), 569–580. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834b89da
9. Park, Y., Park, H. Y., Kim, J., Hwang, H., Jung, Y., Kreider, R., & Lim, K. (2019). Effects of whey protein supplementation prior to, and following, resistance exercise on body composition and training responses: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry, 23(2), 34–44. https://doi.org/10.20463/jenb.2019.0015
10. Lemon P. W. (1995). Do athletes need more dietary protein and amino acids?. International journal of sport nutrition, 5 Suppl, S39–S61. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsn.5.s1.s39
11. Aragon, A. A., & Schoenfeld, B. J. (2013). Nutrient timing revisited: is there a post-exercise anabolic window?. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 10(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-10-5
12. Davis, L. M., Coleman, C., Kiel, J., Rampolla, J., Hutchisen, T., Ford, L., Andersen, W. S., & Hanlon-Mitola, A. (2010). Efficacy of a meal replacement diet plan compared to a food-based diet plan after a period of weight loss and weight maintenance: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrition journal, 9, 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-11
13. Hoffman, J. R., & Falvo, M. J. (2004). Protein - Which is Best?. Journal of sports science & medicine, 3(3), 118–130. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3905294/
14. Bax, M. L., Buffière, C., Hafnaoui, N., Gaudichon, C., Savary-Auzeloux, I., Dardevet, D., Santé-Lhoutellier, V., & Rémond, D. (2013). Effects of meat cooking, and of ingested amount, on protein digestion speed and entry of residual proteins into the colon: a study in minipigs. PloS one, 8(4), e61252. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061252