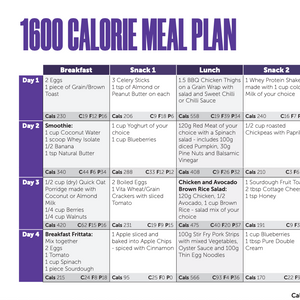
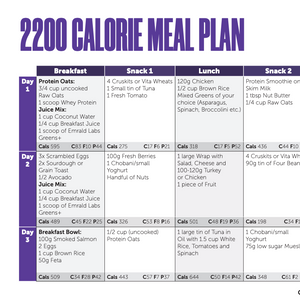
One of the most common questions we receive is “should I take protein powder if I am trying to lose weight”? It’s easy to see how this topic could be confusing as there is the perception that protein powder is only for bodybuilders and Dwayne ‘The Rock’ Johnson. However, everyone could stand to benefit from taking protein powder!
Protein is an essential macronutrient that is responsible for many bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes, hormones, and other molecules. It is also the most satiating macronutrient, meaning it can help you feel fuller for longer periods, leading to a reduced calorie intake.
Protein powder is a concentrated form of protein that is typically made from whey, casein, soy, or pea. It is a convenient and cost-effective way to increase your protein intake, particularly for those who struggle to consume adequate protein through whole foods. The most popular type of protein powder is whey protein powder, which is a fast-digesting protein that is rich in essential amino acids.
Plant protein powder is also available, which is ideal for individuals that are on a plant based diet. This is also a great option if you are unable to tolerate dairy!
Protein powder specific for weight loss is also an option. These protein powders are specifically formulated to help with weight loss as they include ingredients like conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), green tea extract, or caffeine which helps increase energy expenditure, suppress appetite, and increase fat oxidation.
Here are some of the ways protein powder can aid in weight loss:
1. Increases Satiety
As mentioned earlier, protein is the most satiating macronutrient, meaning it can help you feel full and satisfied for longer periods. Several studies have shown that consuming a high-protein diet can lead to reduced hunger and calorie intake, ultimately resulting in weight loss. (1)
A study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that individuals who consumed a high-protein diet lost more weight and body fat than those who followed a standard protein diet. The researchers attributed the weight loss to the increased satiety and reduced calorie intake.
2. Helps Preserve Lean Muscle Mass
When you are trying to lose weight, it is essential to preserve lean muscle mass. Lean muscle mass is metabolically active tissue that burns calories even at rest. Losing lean muscle mass can slow down your metabolism, making it harder to lose weight and easier to gain it back.
Protein powder can help preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals who consumed a high-protein diet lost more body fat and preserved more lean muscle mass than those who followed a standard protein diet (1).
3. Boosts Metabolism
Protein has a higher thermic effect than carbohydrates and fat, meaning it requires more energy to digest, absorb, and metabolize. This process increases your metabolism, leading to an increased calorie burn.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that consuming a high-protein diet increased metabolism and calorie burn. The researchers concluded that increasing protein intake could be an effective strategy for weight loss and metabolic health (1).
4. Helps Control Blood Sugar
Consuming protein with meals can help slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, leading to a more stable blood sugar level. This process can help reduce cravings and hunger, leading to a reduced calorie intake.
A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that consuming whey protein before a high glycemic meal can help reduce blood sugar spikes and increase insulin sensitivity. The researchers concluded that consuming whey protein before meals could be an effective strategy for improving blood sugar control (5).
5. Can Replace High-Calorie Foods
Protein powder can be used as a substitute for high-calorie foods, such as snacks and desserts. By replacing high-calorie foods with protein powder, you can reduce your calorie intake while still consuming adequate protein.
A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that individuals who consumed a high-protein snack had reduced calorie intake compared to those who consumed a high-fat or high-carbohydrate snack. The researchers concluded that consuming high-protein snacks could be an effective strategy for reducing calorie intake and promoting weight loss (4).
In conclusion, protein powder can be an effective aid in weight loss. It can assist with satiating you, preserve lean muscle mass, boost metabolism, and control blood sugar. Protein powders are also exceptionally tasty - making them an awesome low calorie alternative to high calorie sweet treats.
Check out our wide range of protein powders to find the best one for you! We have protein powders available for all goals and dietary requirements. Whether you want to lose weight or gain muscle, we have the products for you.
Still have more questions? Reach out! We’d love to hear from you and help out in any way we can.
References
- Halton, T. L., & Hu, F. B. (2004). The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 23(5), 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719381
- Pasiakos, S. M., Cao, J. J., Margolis, L. M., Sauter, E. R., Whigham, L. D., McClung, J. P., ... & Young, A. J. (2013). Effects of high-protein diets on fat-free mass and muscle protein synthesis following weight loss: a randomized controlled trial. The FASEB Journal, 27(9), 3837-3847. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-230227
- Leidy, H. J., Bossingham, M. J., Mattes, R. D., & Campbell, W. W. (2010). Increased dietary protein consumed at breakfast leads to an initial and sustained feeling of fullness during energy restriction compared to other meal times. British Journal of Nutrition, 104(3), 423-431. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510000792
- Pal, S., & Ellis, V. (2010). The acute effects of four protein meals on insulin, glucose, appetite and energy intake in lean men. British Journal of Nutrition, 104(8), 1241-1248. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510002013
- Layman, D. K., Boileau, R. A., Erickson, D. J., Painter, J. E., Shiue, H., Sather, C., & Christou, D. D. (2003). A reduced ratio of dietary carbohydrate to protein improves body composition and blood lipid profiles during weight loss in adult women. The Journal of Nutrition, 133(2), 411-417. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.2.411